A groundbreaking collaboration between Swiss and American researchers has resulted in the development of a 3D printed robotic hand that integrates skeletal and ligament structures, pushing the boundaries of prosthetics and robotics. This innovative project not only showcases the potential of 3D printing technology but also highlights the interdisciplinary approach that is becoming increasingly vital in the field of advanced engineering.
The project, a joint effort between the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Lausanne (EPFL) and the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, has been years in the making. The team of researchers, engineers, and designers have worked tirelessly to create a robotic hand that not only mimics the appearance of a human hand but also its functionality.
Integrating Skeletal and Ligament Structures
One of the key features of this 3D printed robotic hand is the integration of skeletal and ligament structures. Traditional robotic hands often lack the intricate movements and flexibility that human hands possess. By incorporating these structures, the researchers have been able to create a hand that can perform a wide range of motions, from simple grasping to more complex gestures.
The skeletal structure of the hand is made from a lightweight, yet strong, material that allows for a high degree of flexibility. The ligaments, which are the elastic tissues that connect bones to other bones, are also 3D printed and provide the necessary tension and support for the hand to move in a lifelike manner.
Advancing 3D Printing Technology
The use of 3D printing in this project is not just about creating a physical object; it's about revolutionizing the way we think about manufacturing and design. 3D printing, or additive manufacturing, allows for the creation of complex structures that would be difficult or impossible to produce using traditional methods. This technology enables the researchers to create intricate designs with a high level of precision and detail.
The 3D printing process used in this project is particularly impressive due to its ability to print multiple materials simultaneously. This means that the team can print the skeletal structure and ligaments in one go, ensuring that they are perfectly aligned and integrated. This level of precision is crucial for the hand to function effectively and naturally.
Prosthetic and Robotic Applications
The potential applications for this 3D printed robotic hand are vast. In the field of prosthetics, this technology could provide amputees with a more natural and functional replacement for their lost limbs. The ability to customize the hand to the individual's needs and preferences is a significant advantage, as it allows for a better fit and a more comfortable user experience.
Beyond prosthetics, this technology could also be applied to the development of advanced robotic systems. Robots that can mimic human movements with such precision could be used in a variety of industries, from manufacturing to healthcare. For example, a robot with a dexterous hand could perform delicate surgical procedures or handle fragile items with care.
Interdisciplinary Collaboration
The success of this project is a testament to the power of interdisciplinary collaboration. Bringing together experts from different fields, such as engineering, design, and materials science, has allowed the team to approach the problem from multiple angles and find innovative solutions.
The researchers from EPFL and the University of Illinois have not only shared their technical knowledge but also their creative ideas. This exchange of ideas and perspectives has been crucial in overcoming the challenges associated with creating a robotic hand that is both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
Future Implications and Ethical Considerations
As with any groundbreaking technology, there are ethical considerations that must be addressed. The development of such advanced robotic hands raises questions about the potential for job displacement, as well as the implications for privacy and security in a world where robots can mimic human behavior.
However, the researchers are keenly aware of these issues and are working to ensure that their technology is used responsibly. They emphasize the potential benefits of their work, such as improving the quality of life for amputees and enhancing the capabilities of robots in a way that can benefit society as a whole.
The Swiss-US collaboration on 3D printed robotic hands is a shining example of what can be achieved when cutting-edge technology and interdisciplinary teamwork come together. This project not only represents a significant step forward in the field of robotics and prosthetics but also serves as a reminder of the importance of collaboration and innovation in addressing complex challenges

By Sophia Lewis/Apr 5, 2025

By Jessica Lee/Apr 5, 2025

By Emily Johnson/Apr 5, 2025

By Sophia Lewis/Apr 5, 2025

By George Bailey/Apr 5, 2025
By Amanda Phillips/Apr 5, 2025

By Emily Johnson/Apr 5, 2025

By Natalie Campbell/Apr 5, 2025
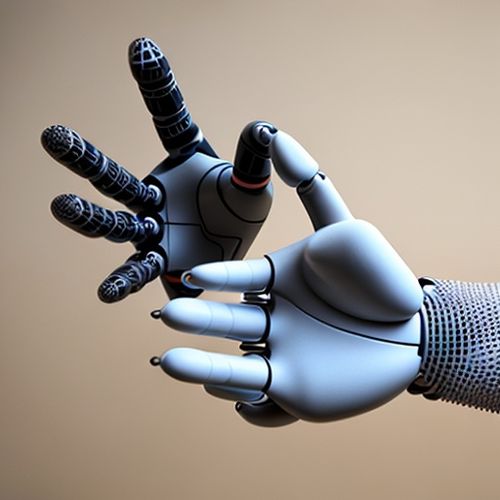
By Sarah Davis/Apr 5, 2025

By Laura Wilson/Apr 5, 2025

By Samuel Cooper/Apr 5, 2025

By James Moore/Apr 5, 2025

By Noah Bell/Apr 5, 2025

By Sarah Davis/Apr 5, 2025

By Ryan Martin/Apr 5, 2025

By Christopher Harris/Apr 5, 2025

By Noah Bell/Apr 5, 2025

By Thomas Roberts/Apr 5, 2025
By Michael Brown/Apr 5, 2025

By George Bailey/Apr 5, 2025